Green
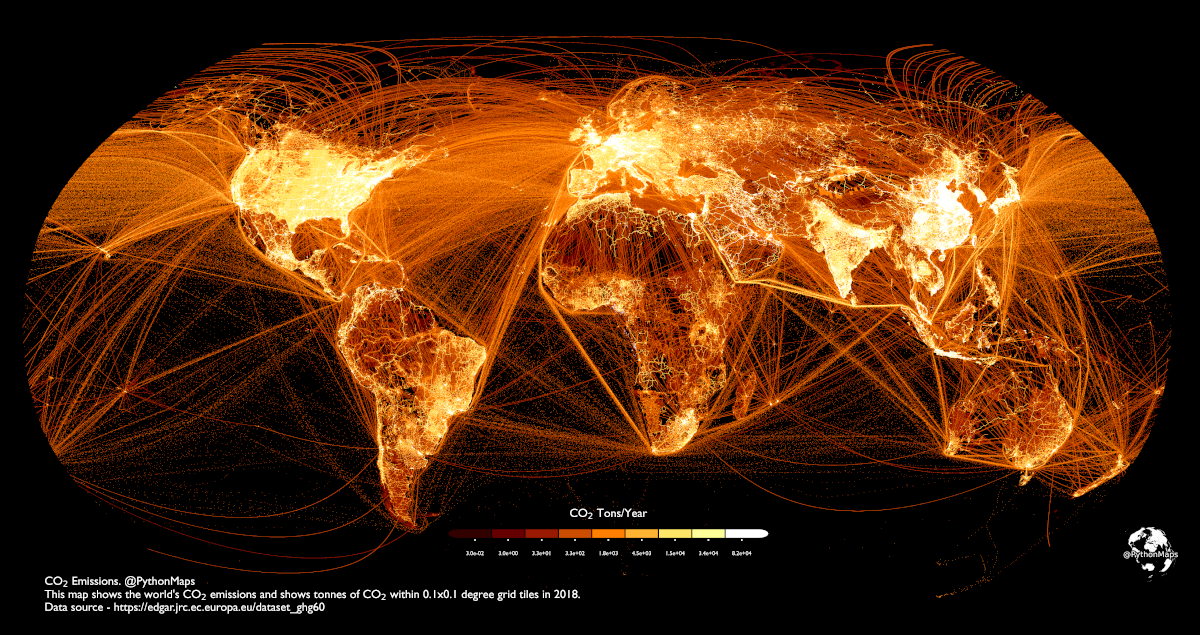
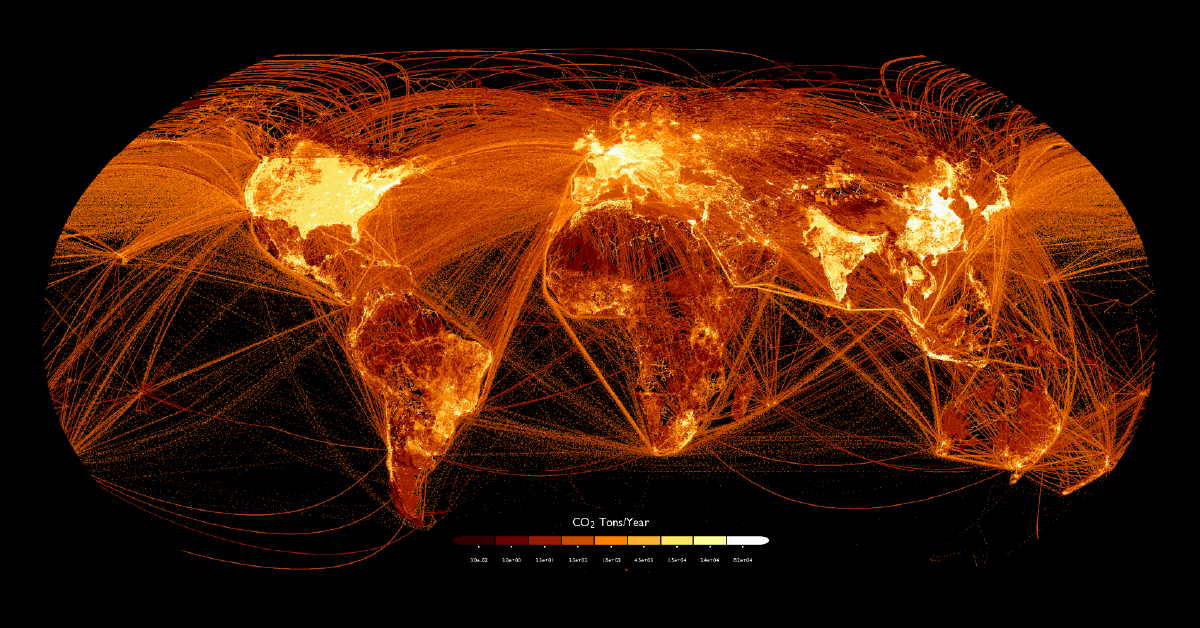
Mapped: Carbon Dioxide Emissions Around the World
Click to view this graphic in a higher-resolution.
Mapped: Carbon Dioxide Emissions Around the World
According to Our World in Data, the global population emits about 34 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) each year.
Where does all this CO₂ come from? This graphic by Adam Symington maps out carbon emissions around the world, using 2018 data from the European Commission that tracks tonnes of CO₂ per 0.1 degree grid (roughly 11 square kilometers).
This type of visualization allows us to clearly see not just population centers, but flight paths, shipping lanes, and high production areas. Let’s take a closer look at some of these concentrated (and brightly lit) regions on the map.
China, India, and the Indian Ocean
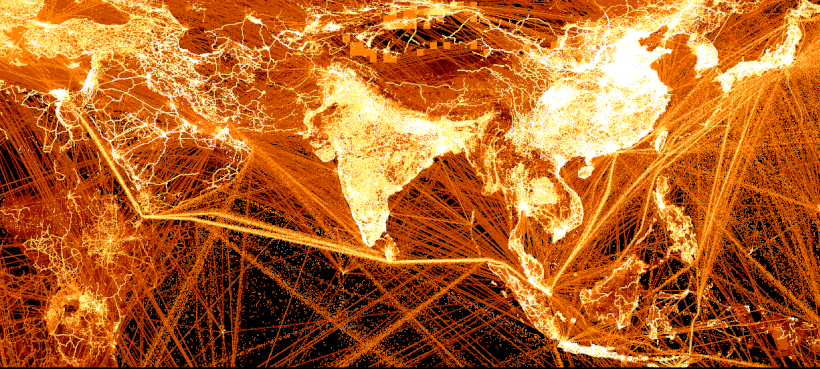
As the two most populated countries and economic forces, China and India are both significant emitters of CO₂. China in particular accounts for about 27% of global CO₂ emissions.
And looking at the oceans, we see how much shipping adds to emissions, with many shipping lanes east of China clearly outlined as well as the major Indian Ocean lane between the Strait of Malacca and the Suez Canal.
The United States and Central America
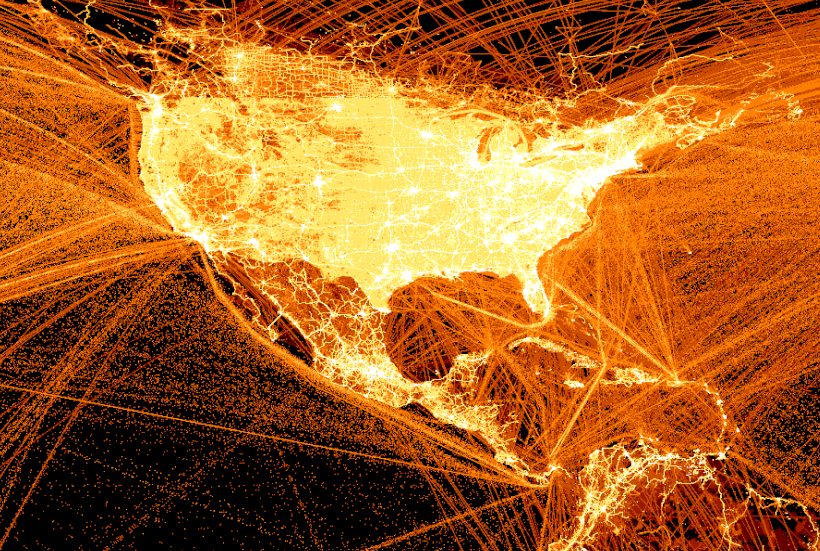
The United States is one of the world’s biggest carbon emitters. While other countries like Qatar and Saudi Arabia technically have higher emissions per capita, their overall emissions are relatively low due to smaller populations.
Across the U.S., the most brightly lit areas are major population centers like the Boston-Washington corridor, the Bay Area, and the Great Lakes. But also lit up are many of the interconnecting highways linking all these population centers, even in the less-populated middle of the country.
With so much traffic in and out of the U.S., the oceans become a murky mix of shipping and flight paths. To the south, very clearly visible is the major concentration of people around Mexico City and the traffic flowing through the Panama Canal.
South America’s Network of Emissions
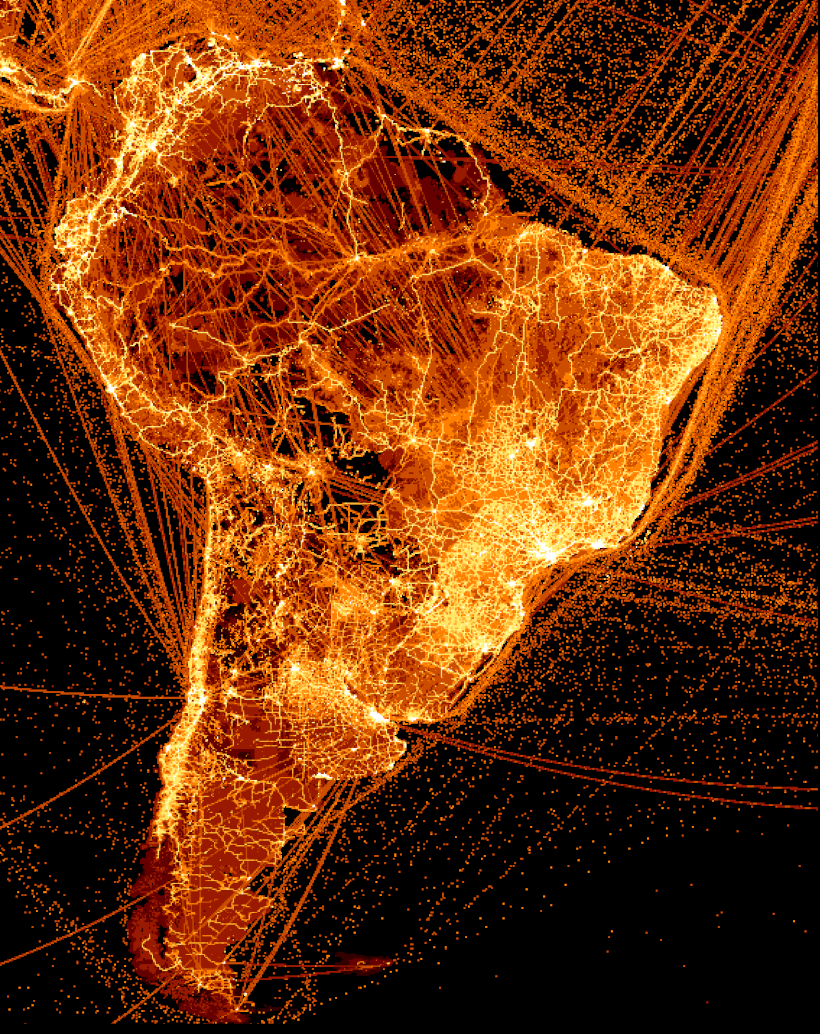
Like the other regions, some of South America’s most populated areas are also the biggest emitters, such as São Paulo and Rio in Brazil and Buenos Aires in Argentina. This map also highlights the continent’s rough terrain, with most of the population and highway emissions limited to the coasts.
However, the cities aren’t the only big emitters in the region. There are clear lines intersecting the Amazon forest in many sections where cities and roads were constructed, including the economic hub city of Manaus along the Amazon River. Likewise, the oceans have many major shipping lanes highlighted, particularly East of Brazil.
Europe and North Africa
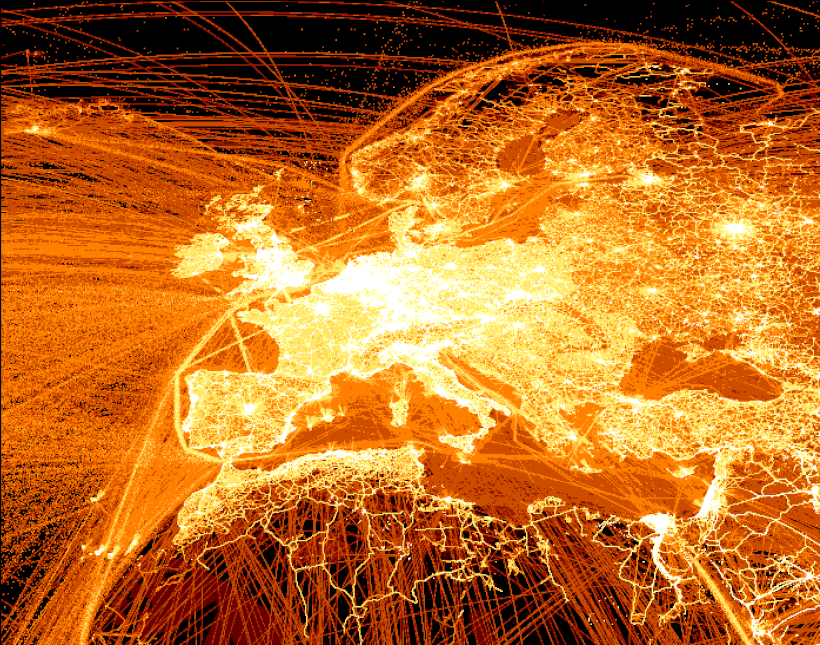

Germany is one of Europe’s biggest carbon emitters—in 2021, the country generated almost 644 million tonnes of CO₂.
Also making an impression are Italy (which is the second-highest CO₂ emitter after Germany) and the UK, as well the significant amount of trade along the English Channel.
Compared to the intricate network of cities, towns, and bustling highways spanning Europe, across the Mediterranean are far clearer and simpler lines of activity in Northern Africa. Two major exceptions are in the Middle-East, where Egypt’s Nile River and Suez Canal are massively lit up, as well as Israel on the east of the sea.
But a more significant (albeit murkier) picture is drawn by the massive amounts of shipping and flight paths illuminating the Atlantic and Mediterranean at large.
Net Zero by 2050
To mitigate the negative effects of climate change, countries around the world have made commitments to reach net-zero emissions.
Imagining the global map of emissions with these commitments in action requires a complete transformation of energy production, consumption habits, transportation infrastructure, and more. And even then, a future generated map wouldn’t be fully dark, as “net-zero” is not equivalent to zero emissions but a balance of emissions and removal.
How might this map of global emissions look in the near and distant future? And what other interesting insights can you generate by browsing the world this way?

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Automotive
How People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
Examining how people get around using cars, public transit, and walking or biking, and the regional differences in usage.
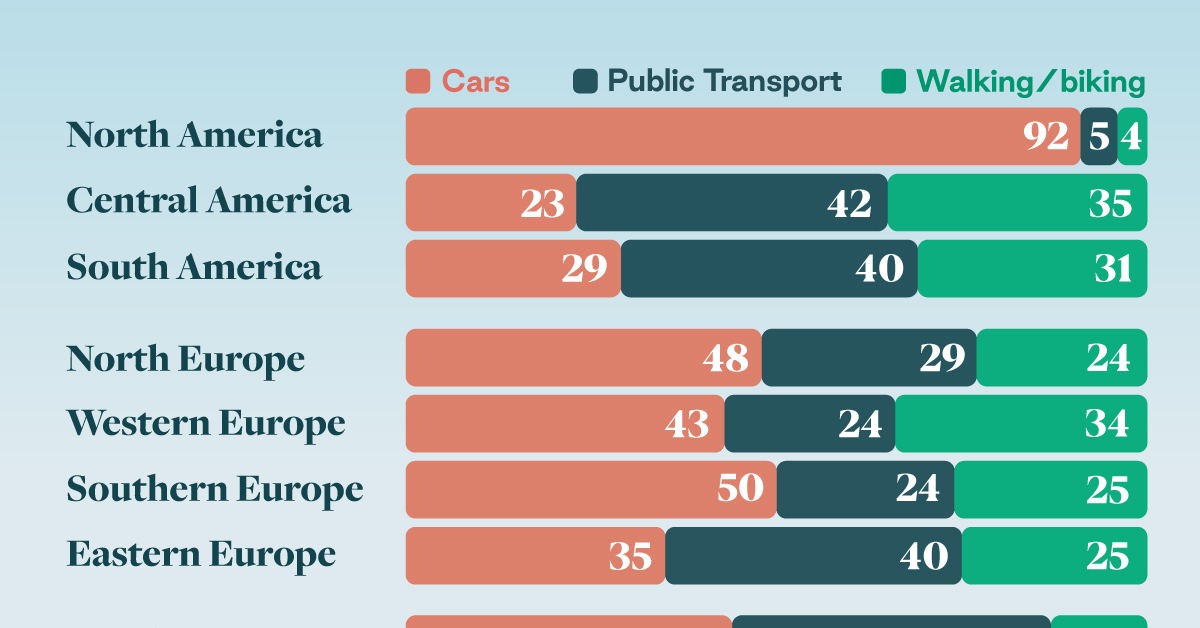
How People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
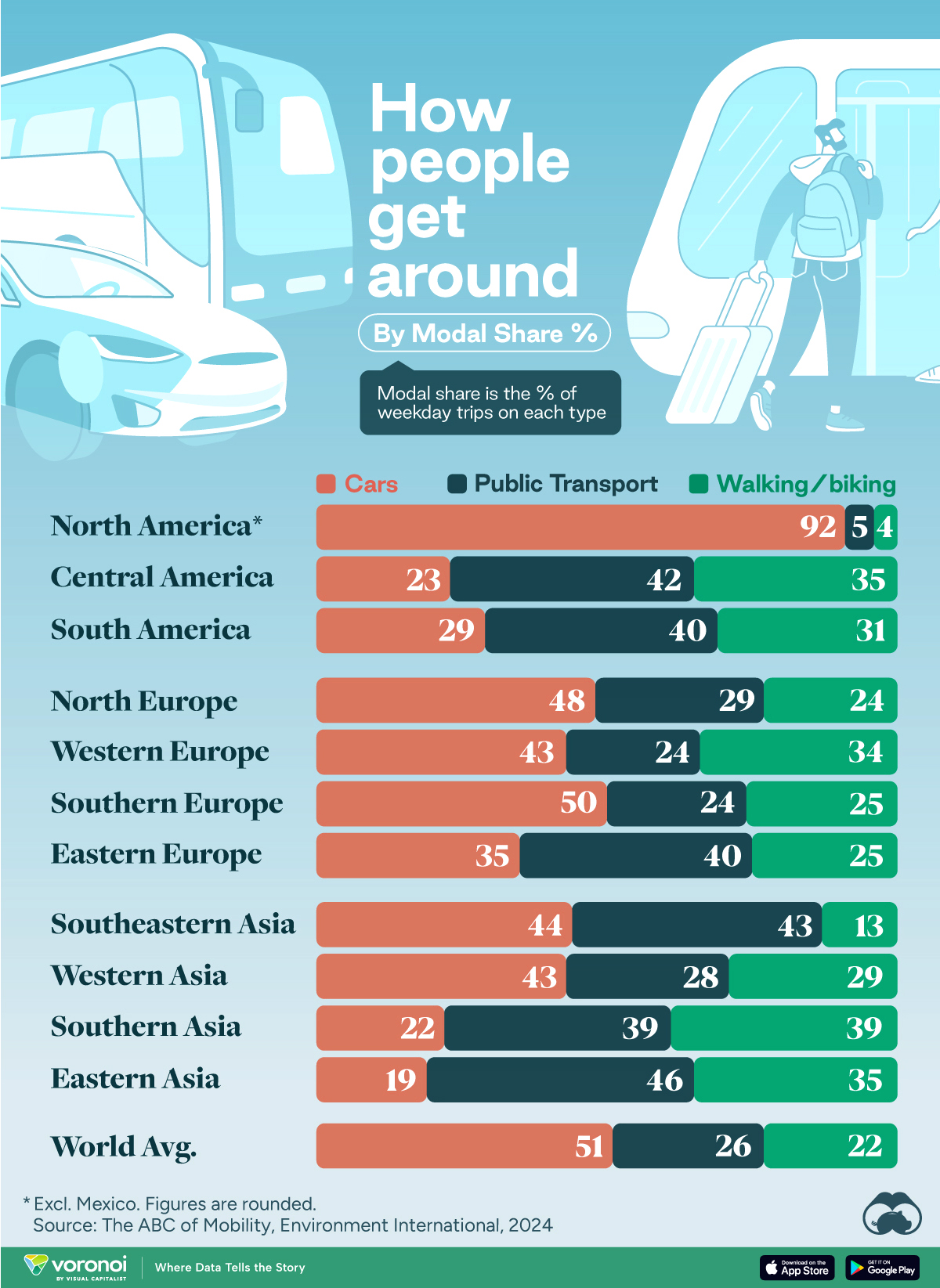
This chart highlights the popularity of different transportation types in the Americas, Europe, and Asia, calculated by modal share.
Data for this article and visualization is sourced from ‘The ABC of Mobility’, a research paper by Rafael Prieto-Curiel (Complexity Science Hub) and Juan P. Ospina (EAFIT University), accessed through ScienceDirect.
The authors gathered their modal share data through travel surveys, which focused on the primary mode of transportation a person employs for each weekday trip. Information from 800 cities across 61 countries was collected for this study.
North American Car Culture Contrasts with the Rest of the World
In the U.S. and Canada, people heavily rely on cars to get around, no matter the size of the city. There are a few exceptions of course, such as New York, Toronto, and smaller college towns across the United States.
| Region | 🚗 Cars | 🚌 Public Transport | 🚶 Walking/Biking |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America* | 92% | 5% | 4% |
| Central America | 23% | 42% | 35% |
| South America | 29% | 40% | 31% |
| Northern Europe | 48% | 29% | 24% |
| Western Europe | 43% | 24% | 34% |
| Southern Europe | 50% | 24% | 25% |
| Eastern Europe | 35% | 40% | 25% |
| Southeastern Asia | 44% | 43% | 13% |
| Western Asia | 43% | 28% | 29% |
| Southern Asia | 22% | 39% | 39% |
| Eastern Asia | 19% | 46% | 35% |
| World | 51% | 26% | 22% |
Note: *Excluding Mexico. Percentages are rounded.
As a result, North America’s share of public transport and active mobility (walking and biking) is the lowest amongst all surveyed regions by a significant amount.
On the other hand, public transport reigns supreme in South and Central America as well as Southern and Eastern Asia. It ties with cars in Southeastern Asia, and is eclipsed by cars in Western Asia.
As outlined in the paper, Europe sees more city-level differences in transport popularity.
For example, Utrecht, Netherlands prefers walking and biking. People in Paris and London like using their extensive transit systems. And in Manchester and Rome, roughly two out of three journeys are by car.
-
 Markets5 days ago
Markets5 days agoVisualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoThe Carbon Footprint of Major Travel Methods
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoVisualizing the Most Common Pets in the U.S.
-

 Culture2 weeks ago
Culture2 weeks agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 voronoi1 week ago
voronoi1 week agoBest Visualizations of April on the Voronoi App
-

 Wealth1 week ago
Wealth1 week agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThe Top Private Equity Firms by Country
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoThe Best U.S. Companies to Work for According to LinkedIn