Markets
Mapped: GDP Growth Forecasts by Country in 2024
GDP Growth Forecasts in 2024
This was originally posted on Advisor Channel. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on financial markets that help advisors and their clients.
Resilient GDP growth and falling inflation are spurring a brighter outlook for 2024, although cautions remain across global economies.
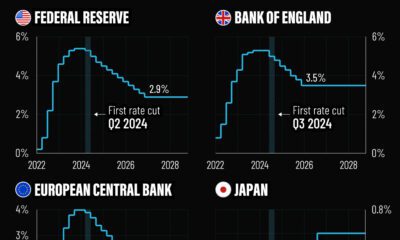
While investors are hopeful that U.S. rate cuts could happen as early as May, the Fed has signaled that it won’t “declare victory” too soon. As countries around the world maneuver a complex landscape, they are faced with a scope of risks that include inflationary spikes, rising debt loads, and dwindling consumer savings.
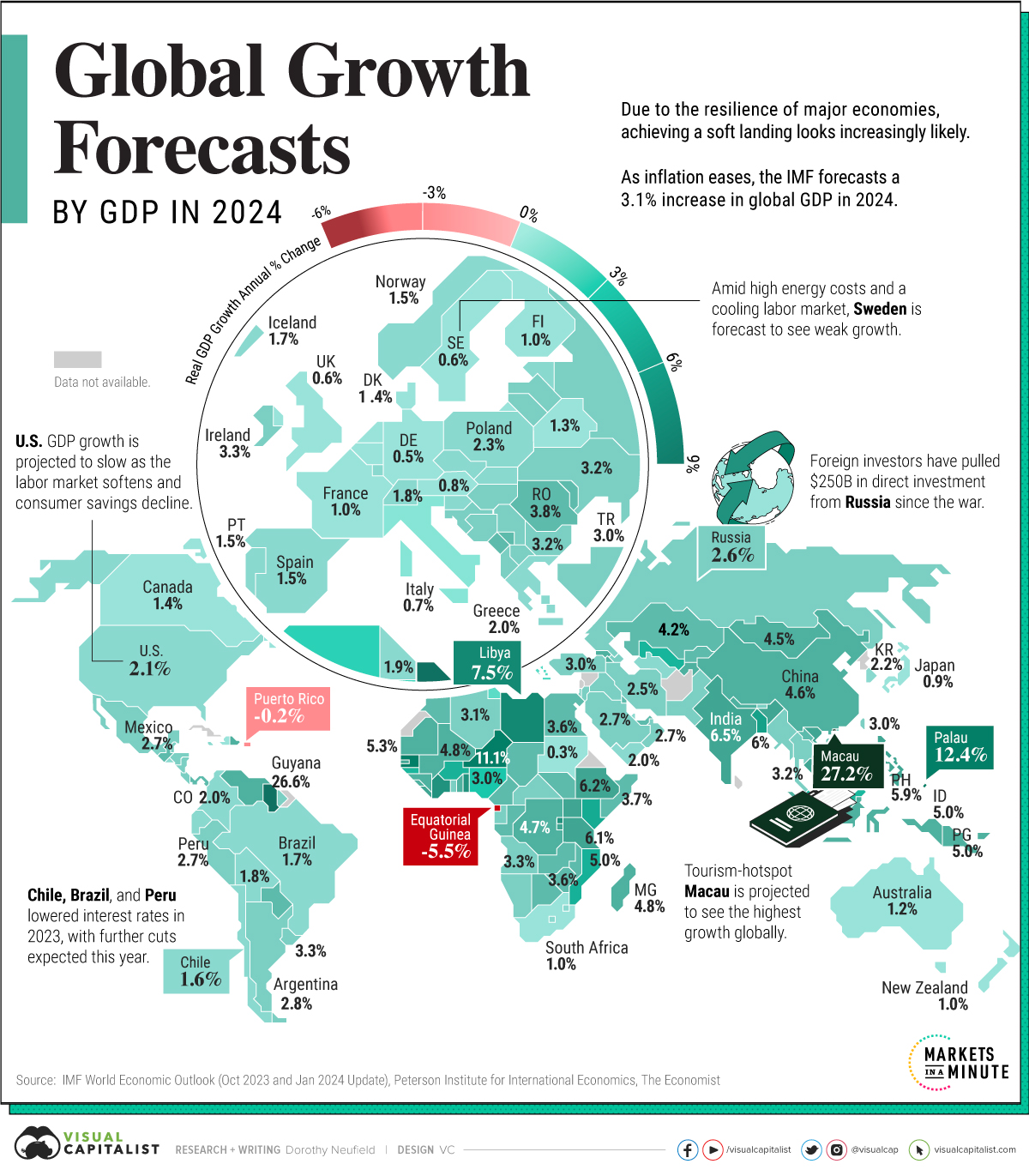
This graphic shows global GDP growth projections in 2024, based on the International Monetary Fund (IMF) October 2023 Outlook and January 2024 update.
Global GDP Growth Outlook 2024
In 2024, real GDP growth is forecast to increase 3.1%, a slight rise from October’s outlook.
While positive growth is projected across all regions, it varies widely due to many factors spanning from the effects of higher borrowing costs to low consumer sentiment. Here are forecasts across 191 countries worldwide:
| Country | 2024 Real GDP % Change (Projected) | 2023 Real GDP % Change (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇱 Albania | 3.3% | 3.6% |
| 🇩🇿 Algeria | 3.1% | 3.8% |
| 🇦🇩 Andorra | 1.5% | 2.1% |
| 🇦🇴 Angola | 3.3% | 1.3% |
| 🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda | 5.4% | 5.6% |
| 🇦🇷 Argentina | 2.8% | -2.5% |
| 🇦🇲 Armenia | 5.0% | 7.0% |
| 🇦🇼 Aruba | 1.2% | 2.3% |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | 1.2% | 1.8% |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 0.8% | 0.1% |
| 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | 2.5% | 2.5% |
| 🇧🇸 The Bahamas | 1.8% | 2.7% |
| 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 3.6% | 6.0% |
| 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 6.0% | 4.5% |
| 🇧🇧 Barbados | 3.9% | 1.6% |
| 🇧🇾 Belarus | 1.3% | 1.0% |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 0.9% | 4.0% |
| 🇧🇿 Belize | 3.0% | 5.5% |
| 🇧🇯 Benin | 6.3% | 5.3% |
| 🇧🇹 Bhutan | 3.0% | 1.8% |
| 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 1.8% | 2.0% |
| 🇧🇦 Bosnia and Herzegovina | 3.0% | 3.8% |
| 🇧🇼 Botswana | 4.1% | 3.1% |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil* | 1.7% | -0.8% |
| 🇧🇳 Brunei Darussalam | 3.5% | 1.7% |
| 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 3.2% | 4.4% |
| 🇧🇫 Burkina Faso | 6.4% | 3.3% |
| 🇧🇮 Burundi | 6.0% | 4.4% |
| 🇨🇻 Cabo Verde | 4.5% | 5.6% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 6.1% | 4.0% |
| 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 4.2% | 1.3% |
| 🇨🇦 Canada* | 1.4% | 1.0% |
| 🇨🇫 Central African Republic | 2.5% | 4.0% |
| 🇹🇩 Chad | 3.7% | -0.5% |
| 🇨🇱 Chile | 1.6% | 5.0% |
| 🇨🇳 China* | 4.6% | 1.4% |
| 🇨🇴 Colombia | 2.0% | 3.0% |
| 🇰🇲 Comoros | 3.5% | 4.4% |
| 🇨🇩 Democratic Republic of the Congo | 4.7% | 2.7% |
| 🇨🇬 Republic of Congo | 4.4% | 6.2% |
| 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 3.2% | 2.2% |
| 🇨🇮 Côte d'Ivoire | 6.6% | 0.2% |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 2.6% | 6.7% |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 2.7% | 1.7% |
| 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 2.3% | 5.0% |
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | 1.4% | 4.6% |
| 🇩🇯 Djibouti | 6.0% | 3.0% |
| 🇩🇲 Dominica | 4.6% | 1.4% |
| 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 5.2% | 4.2% |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 1.8% | 2.2% |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.6% | -6.2% |
| 🇸🇻 El Salvador | 1.9% | -2.3% |
| 🇬🇶 Equatorial Guinea | -5.5% | 3.1% |
| 🇪🇪 Estonia | 2.4% | 6.1% |
| 🇸🇿 Eswatini | 3.3% | 7.5% |
| 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 6.2% | -0.1% |
| 🇫🇯 Fiji | 3.9% | 1.0% |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 1.0% | 2.8% |
| 🇫🇷 France* | 1.0% | 6.2% |
| 🇬🇦 Gabon | 2.6% | -0.5% |
| 🇬🇲 The Gambia | 6.2% | 1.2% |
| 🇬🇪 Georgia | 4.8% | 2.5% |
| 🇩🇪 Germany* | 0.5% | 3.9% |
| 🇬🇭 Ghana | 2.7% | 3.4% |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 2.0% | 5.9% |
| 🇬🇩 Grenada | 3.8% | 4.5% |
| 🇬🇹 Guatemala | 3.5% | 38.4% |
| 🇬🇳 Guinea | 5.6% | -1.5% |
| 🇬🇼 Guinea-Bissau | 5.0% | 2.9% |
| 🇬🇾 Guyana | 26.6% | 4.4% |
| 🇭🇹 Haiti | 1.4% | -0.3% |
| 🇭🇳 Honduras | 3.2% | 3.3% |
| 🇭🇰 Hong Kong SAR | 2.9% | 6.3% |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | 3.1% | 5.0% |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 1.7% | -2.7% |
| 🇮🇳 India* | 6.5% | 2.0% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 5.0% | 3.0% |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | 2.5% | 3.1% |
| 🇮🇶 Iraq | 2.9% | 0.7% |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | 3.3% | 2.0% |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 3.0% | 2.0% |
| 🇮🇹 Italy* | 0.7% | 2.6% |
| 🇯🇲 Jamaica | 1.8% | 4.6% |
| 🇯🇵 Japan* | 0.9% | 5.0% |
| 🇯🇴 Jordan | 2.7% | 2.6% |
| 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 4.2% | 1.4% |
| 🇰🇪 Kenya | 5.3% | 3.8% |
| 🇰🇮 Kiribati | 2.4% | -0.6% |
| 🇰🇷 Korea | 2.2% | 3.4% |
| 🇽🇰 Kosovo | 4.0% | 4.0% |
| 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 3.6% | 0.5% |
| 🇰🇬 Kyrgyz Republic | 4.3% | 2.1% |
| 🇱🇦 Lao P.D.R. | 4.0% | 4.6% |
| 🇱🇻 Latvia | 2.6% | 12.5% |
| 🇱🇸 Lesotho | 2.3% | -0.2% |
| 🇱🇷 Liberia | 5.3% | -0.4% |
| 🇱🇾 Libya | 7.5% | 74.4% |
| 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 2.7% | 4.0% |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 1.5% | 1.7% |
| 🇲🇴 Macao SAR | 27.2% | 4.0% |
| 🇲🇬 Madagascar | 4.8% | 8.1% |
| 🇲🇼 Malawi | 3.3% | 4.5% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 4.3% | 3.8% |
| 🇲🇻 Maldives | 5.0% | 3.0% |
| 🇲🇱 Mali | 4.8% | 4.5% |
| 🇲🇹 Malta | 3.3% | 5.1% |
| 🇲🇭 Marshall Islands | 3.0% | 3.2% |
| 🇲🇷 Mauritania | 5.3% | 2.6% |
| 🇲🇺 Mauritius | 3.8% | 2.0% |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico* | 2.7% | 5.5% |
| 🇫🇲 Micronesia | 3.1% | 4.5% |
| 🇲🇩 Moldova | 4.3% | 2.4% |
| 🇲🇳 Mongolia | 4.5% | 7.0% |
| 🇲🇪 Montenegro | 3.7% | 2.6% |
| 🇲🇦 Morocco | 3.6% | 2.8% |
| 🇲🇿 Mozambique | 5.0% | 0.5% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 2.6% | 0.8% |
| 🇳🇦 Namibia | 2.7% | 0.6% |
| 🇳🇷 Nauru | 1.3% | 1.1% |
| 🇳🇵 Nepal | 5.0% | 3.0% |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1.2% | 4.1% |
| 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 1.0% | 2.9% |
| 🇳🇮 Nicaragua | 3.3% | 2.5% |
| 🇳🇪 Niger | 11.1% | 2.3% |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria* | 3.0% | 1.2% |
| 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | 3.2% | -0.5% |
| 🇳🇴 Norway | 1.5% | 0.8% |
| 🇴🇲 Oman | 2.7% | 6.0% |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 2.5% | 3.0% |
| 🇵🇼 Palau | 12.4% | 4.5% |
| 🇵🇦 Panama | 4.0% | 1.1% |
| 🇵🇬 Papua New Guinea | 5.0% | 5.3% |
| 🇵🇾 Paraguay | 3.8% | 0.6% |
| 🇵🇪 Peru | 2.7% | 2.3% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 5.9% | -0.7% |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | 2.3% | 2.4% |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 1.5% | 4.0% |
| 🇵🇷 Puerto Rico | -0.2% | 2.2% |
| 🇶🇦 Qatar | 2.2% | 2.2% |
| 🇷🇴 Romania | 3.8% | 6.2% |
| 🇷🇺 Russia* | 2.6% | 0.5% |
| 🇷🇼 Rwanda | 7.0% | 8.0% |
| 🇼🇸 Samoa | 3.6% | 2.2% |
| 🇸🇲 San Marino | 1.3% | 0.8% |
| 🇸🇹 São Tomé and Príncipe | 2.4% | 4.1% |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia* | 2.7% | 2.0% |
| 🇸🇳 Senegal | 8.8% | 4.2% |
| 🇷🇸 Serbia | 3.0% | 2.7% |
| 🇸🇨 Seychelles | 3.9% | 1.0% |
| 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 4.7% | 1.3% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 2.1% | 2.0% |
| 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 2.5% | 2.5% |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 2.2% | 2.8% |
| 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | 2.4% | 0.9% |
| 🇸🇴 Somalia | 3.7% | 3.5% |
| 🇿🇦 South Africa* | 1.0% | 2.5% |
| 🇸🇸 South Sudan | 4.2% | 4.9% |
| 🇪🇸 Spain* | 1.5% | 3.2% |
| 🇰🇳 St. Kitts and Nevis | 3.8% | 6.2% |
| 🇱🇨 St. Lucia | 2.3% | -18.3% |
| 🇻🇨 St. Vincent and the Grenadines | 5.0% | 2.1% |
| 🇸🇩 Sudan | 0.3% | -0.7% |
| 🇸🇷 Suriname | 3.0% | 0.9% |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | 0.6% | 4.0% |
| 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 1.8% | 0.8% |
| 🇹🇼 Taiwan | 3.0% | 6.5% |
| 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | 5.0% | 5.2% |
| 🇹🇿 Tanzania | 6.1% | 2.7% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 3.2% | 4.3% |
| 🇹🇱 Timor-Leste | 3.1% | 5.6% |
| 🇹🇬 Togo | 5.3% | 1.5% |
| 🇹🇴 Tonga | 2.5% | 5.4% |
| 🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago | 2.2% | 2.6% |
| 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 1.9% | 2.5% |
| 🇹🇷 Türkiye | 3.0% | 1.3% |
| 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | 2.1% | 2.5% |
| 🇹🇻 Tuvalu | 3.5% | 3.9% |
| 🇺🇬 Uganda | 5.7% | 4.6% |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 3.2% | 2.0% |
| 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 4.0% | 3.4% |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom* | 0.6% | 0.5% |
| 🇺🇸 U.S.* | 2.1% | 2.1% |
| 🇺🇾 Uruguay | 3.3% | 1.0% |
| 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 5.5% | 5.5% |
| 🇻🇺 Vanuatu | 2.6% | 1.5% |
| 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 4.5% | 4.0% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 5.8% | 4.7% |
| 🇵🇸 West Bank and Gaza | 2.7% | 3.0% |
| 🇾🇪 Yemen | 2.0% | -0.5% |
| 🇿🇲 Zambia | 4.3% | 3.6% |
| 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | 3.6% | 4.1% |
*Reflect updated figures from the January 2024 IMF Update
In the United States, GDP growth is projected to remain moderately strong, supported by rising real wages boosting consumption across the economy.
Yet compared to last year, growth is set to slow amid a softening labor market. In 2024, Citigroup announced it was laying off 20,000 employees after a disappointing year. Meanwhile, tech firms such as Google, Amazon, and Salesforce are reducing headcounts. Along with this, package delivery giant UPS announced 12,000 job cuts.
In China, property market woes are dragging on economic growth. Declining real estate values have impacted incomes, assets, and the public mood. Due to these headwinds, consumption growth is forecast to drop over the year.
Over in Latin America, Chile and Brazil were among the first emerging countries to hike interest rates in 2021—and they were some of the first to cut them last year. Thanks to improving domestic demand amid dissipating price spikes, the IMF upgraded the outlooks for Brazil and Mexico in 2024.
The lowest growth across all regions is forecast to be seen in Europe, at 0.9%. In late 2023, Signa, a multi-billion European property firm collapsed following the sharpest rise in interest rates in the European Union’s 25-year history. Also dimming the outlook is low consumer sentiment and the impact of high energy prices.
What are the Key Risks?
While no one holds a crystal ball, there are certain risks outlined by the IMF that could negatively impact global GDP growth:
- Sharply Rising Commodity Prices: If geopolitical tensions escalate in the Israel-Hamas war, it could spillover into the broader region leading to spikes in energy prices. Over a third of global oil exports are based out of the region, in addition to 14% of global gas exports. Adding to this, 11% of international trade passes through the Red Sea, which has seen continued attacks between Iran-backed Houthi rebels and strikes from the U.S. and its allies.
- Stubborn Inflation: A return of supply disruptions paired with an overheated labor market could add inflationary pressures, potentially leading to higher interest rates. In turn, stock markets could respond adversely and financial stability could deteriorate.
- China’s Economy Slows: A property market rout could hurt domestic growth and consumer confidence, leading to declining consumption across the country. Accounting for nearly 19% of global GDP (PPP) in 2023, a slowing Chinese economy could impact countries that rely on trade with China.
While these risks remain present, the economy could witness positive surprises as well. Should inflation fall faster than expected, it would likely lead to monetary easing and a boost to global economic growth. Overall, the global economy defied expectations in 2023, and it may do the same in 2024.
Markets
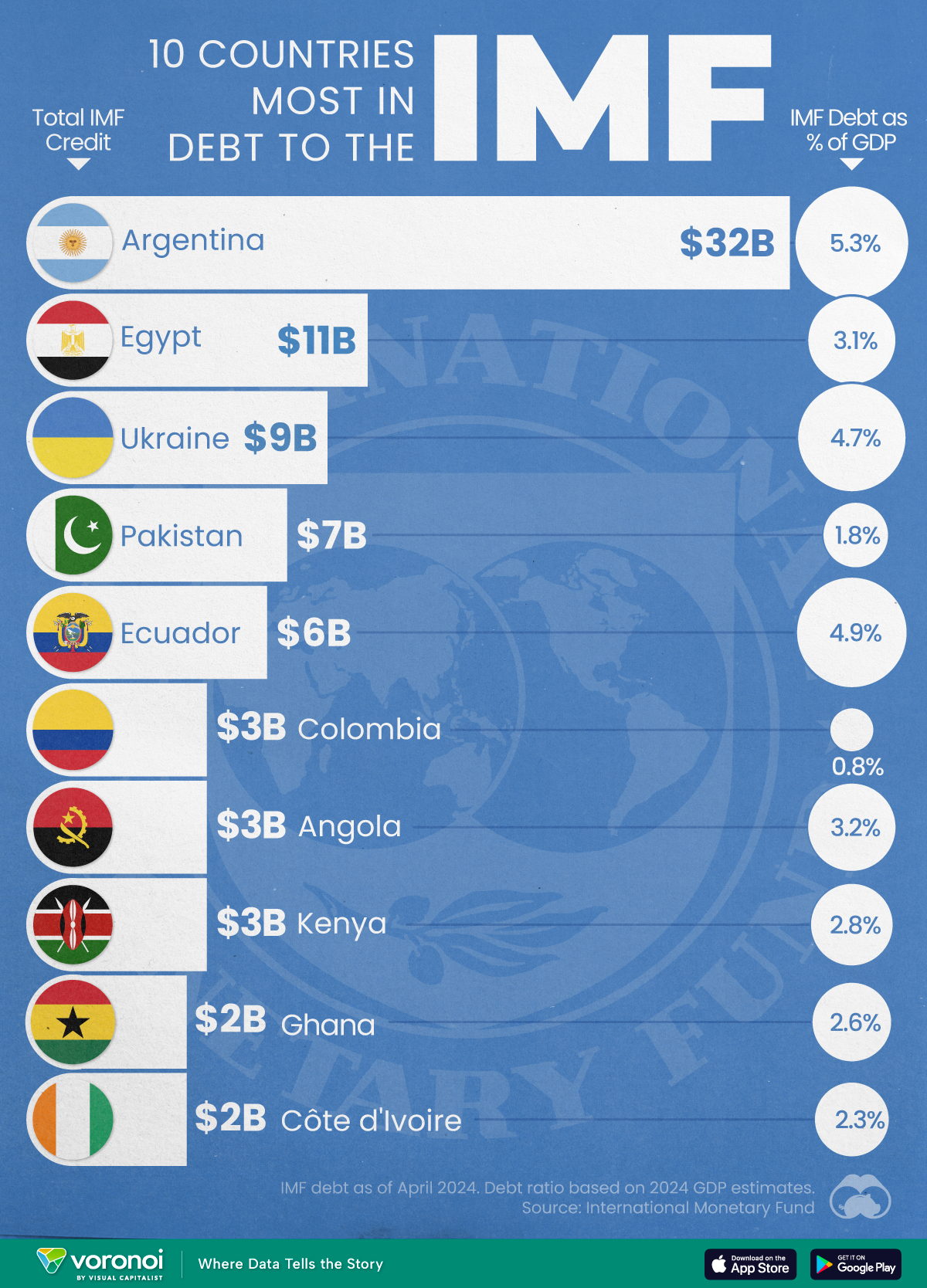
Top 10 Countries Most in Debt to the IMF
Argentina tops the ranking, with a debt equivalent to 5.3% of the country’s GDP.

Top 10 Countries Most in Debt to the IMF
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Established in 1944, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) supports countries’ economic growth by providing financial aid and guidance on policies to enhance stability, productivity, and job opportunities.
Countries seek loans from the IMF to address economic crises, stabilize their currencies, implement structural reforms, and alleviate balance of payments difficulties.
In this graphic, we visualize the 10 countries most indebted to the fund.
Methodology
We compiled this ranking using the International Monetary Fund’s data on Total IMF Credit Outstanding. We selected the latest debt data for each country, accurate as of April 29, 2024.
Argentina Tops the Rank
Argentina’s debt to the IMF is equivalent to 5.3% of the country’s GDP. In total, the country owns more than $32 billion.
| Country | IMF Credit Outstanding ($B) | GDP ($B, 2024) | IMF Debt as % of GDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇷 Argentina | 32 | 604.3 | 5.3 |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | 11 | 347.6 | 3.1 |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 9 | 188.9 | 4.7 |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 7 | 374.7 | 1.8 |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 6 | 121.6 | 4.9 |
| 🇨🇴 Colombia | 3 | 386.1 | 0.8 |
| 🇦🇴 Angola | 3 | 92.1 | 3.2 |
| 🇰🇪 Kenya | 3 | 104.0 | 2.8 |
| 🇬🇭 Ghana | 2 | 75.2 | 2.6 |
| 🇨🇮 Ivory Coast | 2 | 86.9 | 2.3 |
A G20 member and major grain exporter, the country’s history of debt trouble dates back to the late 1890s when it defaulted after contracting debts to modernize the capital, Buenos Aires. It has already been bailed out over 20 times in the last six decades by the IMF.
Five of the 10 most indebted countries are in Africa, while three are in South America.
The only European country on our list, Ukraine has relied on international support amidst the conflict with Russia. It is estimated that Russia’s full-scale invasion of the country caused the loss of a third of the country’s economy. The country owes $9 billion to the IMF.
In total, almost 100 countries owe money to the IMF, and the grand total of all of these debts is $111 billion. The above countries (top 10) account for about 69% of these debts.
-
 Maps7 days ago
Maps7 days agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
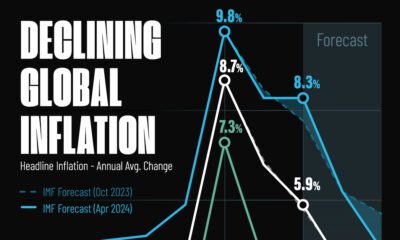
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoVisualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
-
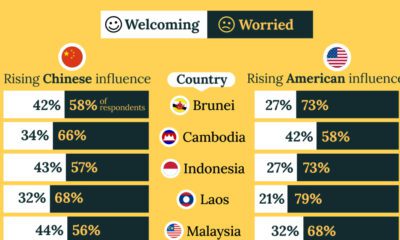
 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoCharted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoThe Evolution of U.S. Beer Logos
-

 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhat Causes Preventable Child Deaths?
-
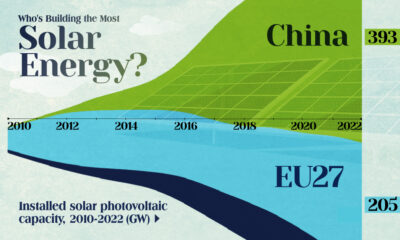
 Energy1 week ago
Energy1 week agoWho’s Building the Most Solar Energy?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoMapped: The Most Valuable Company in Each Southeast Asian Country
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country