Politics
How Much Government Debt Rests Upon Your Shoulders?
How Much Government Debt Rests Upon Your Shoulders?
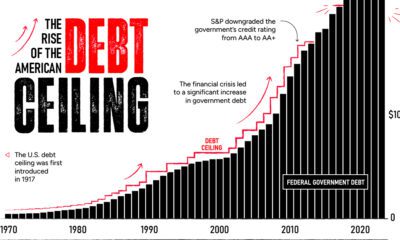
With the U.S. National Debt closing in on the $20 trillion mark, there has been a lot of conversation in Washington about debt and its role in government.
And most of that conversation right now revolves around President-elect Donald Trump.
On one hand, the Trump campaign had early rhetoric in the Presidential campaign that the elimination of the deficit and existing government debt would be paramount if elected. The Trump administration has also been highly critical of the Federal Reserve, saying that the Fed’s policies create a “false economy”. As a result, some see Trump embracing the unique opportunity to put his stamp on how the Federal Reserve does business in early 2017.
On the other hand, even many conservative think tanks are concerned about what Trump policies mean for government debt. Rebuilding infrastructure is not cheap, and widely-cited estimates see the national debt increasing by anywhere from $5.3 trillion to $11.5 trillion over the next 10 years.
How Much Government Debt is On You?
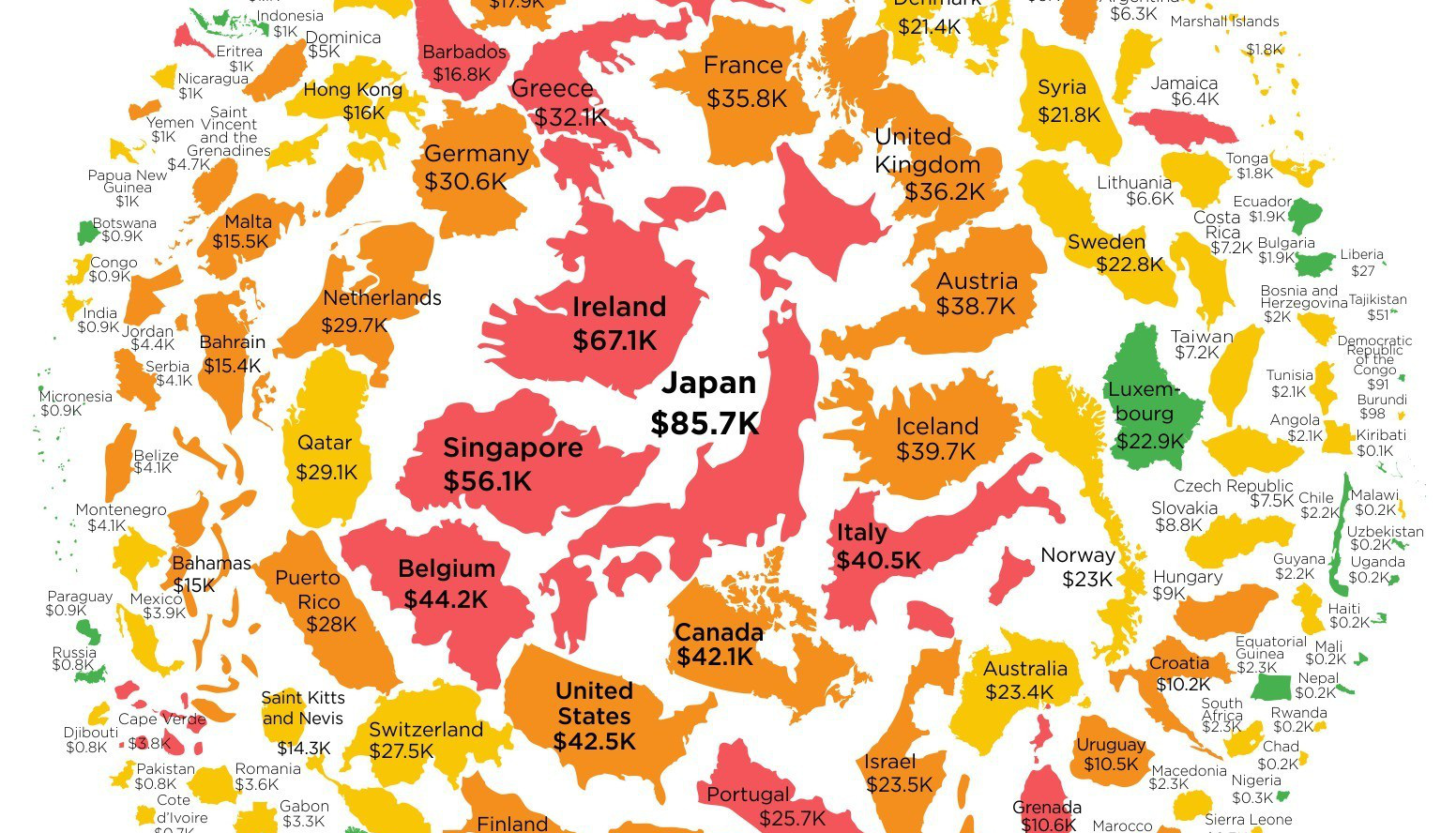
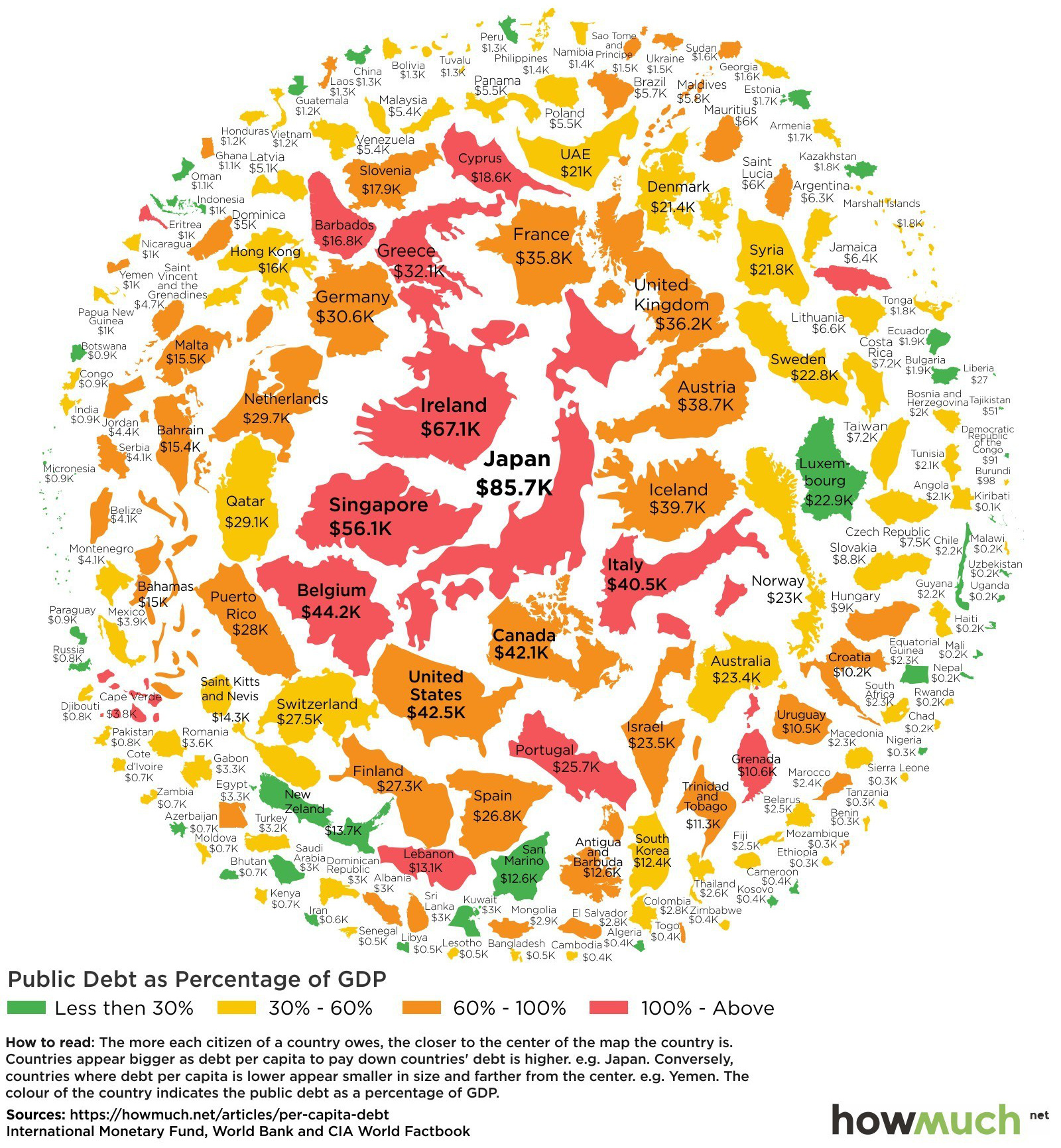
While giant numbers like $20 trillion sound abstract and meaningless, converting them to debt-per-capita can make things more intuitive. The per-capita amount shows the amount of debt that exists per citizen, and makes things plain and simple.
Today’s infographic from HowMuch.net, a cost information site, shows government debt-per-capita in every country in the world, including the United States.
Here are the countries where people owe the most debt per person:
- Japan: $85,694.87 per person
- Ireland: $67,147.59 per person
- Singapore: $56,112.75 per person
- Belgium: $44,202.75 per person
- United States: $42,503.98 per person
- Canada: $42,142.61 per person
- Italy: $40,461.11 per person
- Iceland: $39,731.65 per person
- Australia: $38,769.98 per person
- United Kingdom: $36,206.11 per person
Of course, debt-per-capita isn’t the only lens to view government debt.
We’ve previously shown global debt by percentage per country, government debt compared to tax revenues, accumulated debt compared to markets and the money supply, and a map scaled to debt-to-GDP ratios.
United States
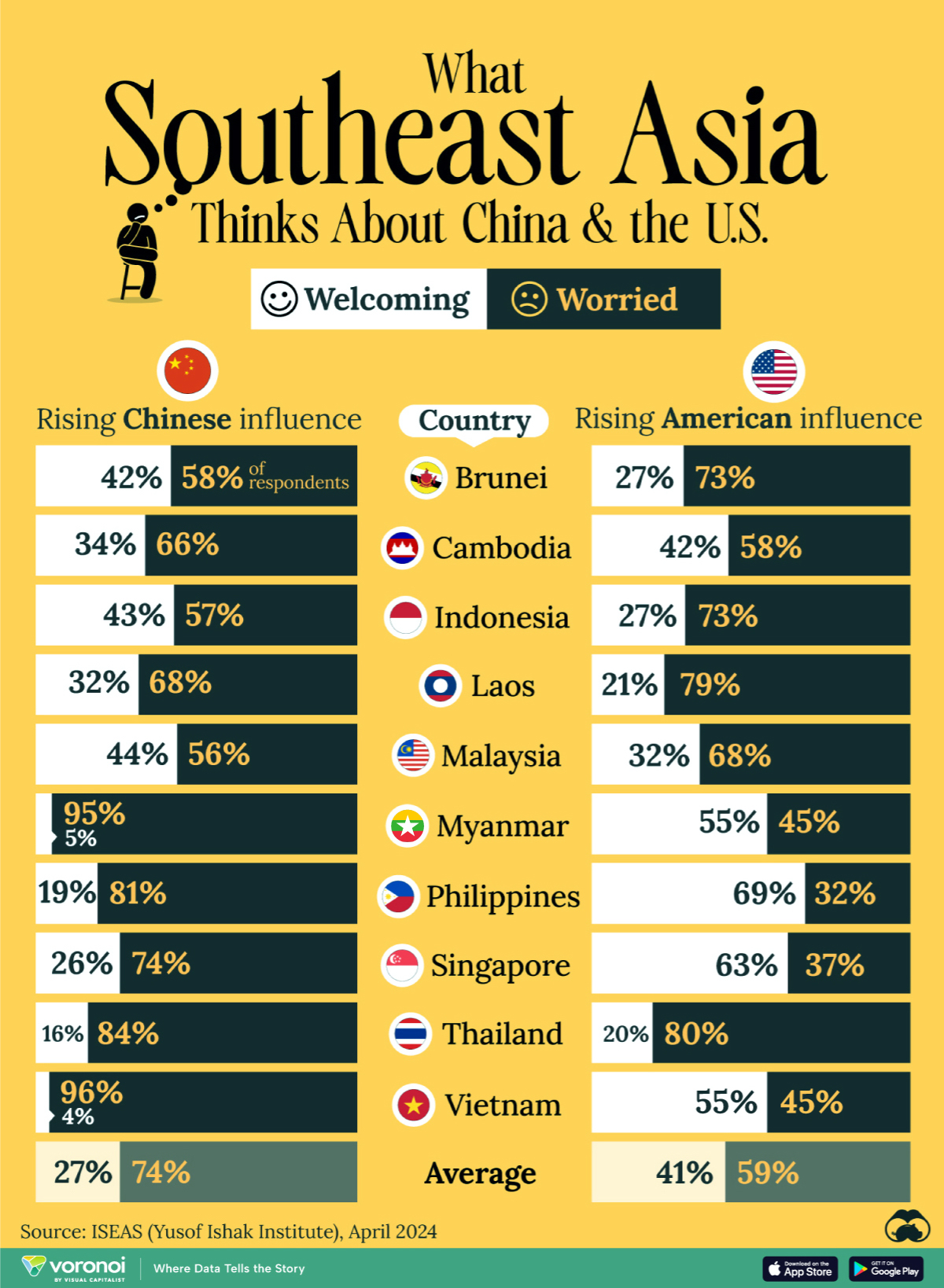
Charted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
A significant share of respondents from an ASEAN-focused survey are not happy about rising American and Chinese influence in the region.
What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute. Nearly 2,000 respondents were asked if they were worried or welcoming of rising Chinese and American geopolitical influence in their country.
The countries surveyed all belong to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia.
Feelings Towards China
On average, a significant share of respondents from all 10 countries are worried about rising influence from both the U.S. and China.
However, overall skepticism is higher for China, at 74% (versus 59% for U.S.).
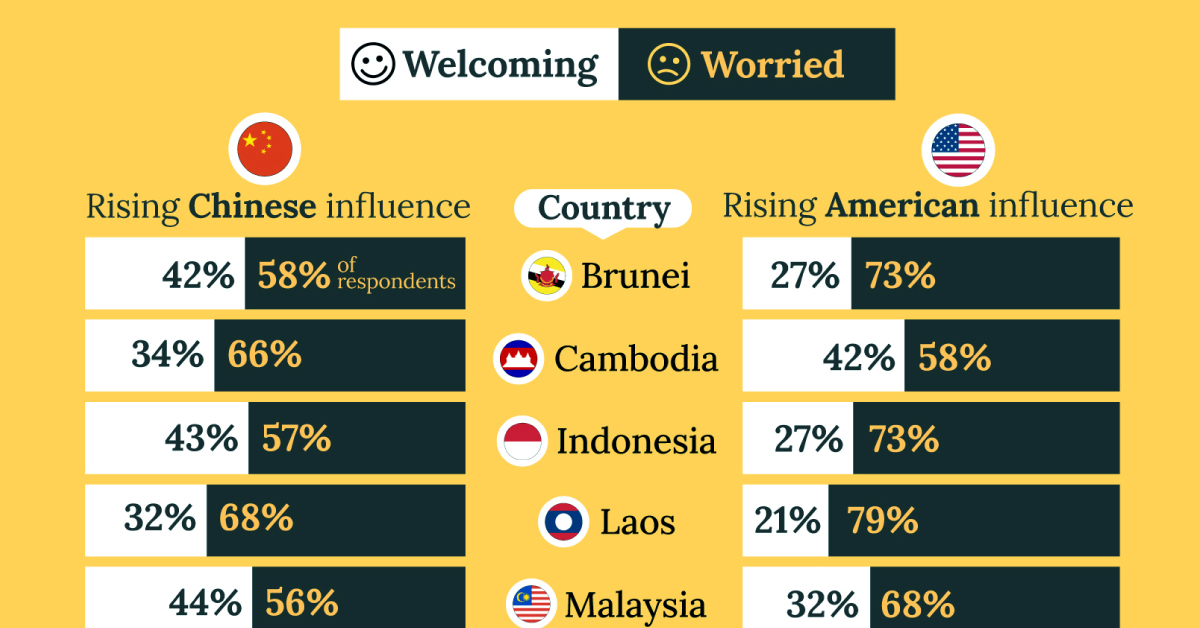
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇨🇳 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇨🇳 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 58% | 42% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 66% | 34% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57% | 43% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 56% | 44% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 95% | 5% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 81% | 19% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 74% | 26% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 84% | 16% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 96% | 4% |
| Average | 74% | 27% |
The recently-cooled but still active territorial concerns over the South China Sea may play a significant role in these responses, especially in countries which are also claimants over the sea.
For example, in Vietnam over 95% of respondents said they were worried about China’s growing influence.
Feelings Towards America
Conversely, rising American influence is welcomed in two countries with competing claims in the South China Sea, the Philippines (69%) and Vietnam (55%).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇺🇸 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇺🇸 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 73% | 27% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 58% | 42% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 73% | 27% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 79% | 21% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 45% | 55% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 32% | 69% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 37% | 63% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 80% | 20% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 45% | 55% |
| Average | 59% | 41% |
Despite this, on a regional average, more respondents worry about growing American influence (59%) than they welcome it (41%).
Interestingly, it seems almost every ASEAN nation has a clear preference for one superpower over the other.
The only exception is Thailand, where those surveyed were not a fan of either option, with 84% worried about China, and 80% worried about the U.S.
-

 Money6 days ago
Money6 days agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
-

 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024