Green
Ranked: The 20 Most Air-Polluted Cities on Earth
![]() Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Subscribe to the Elements free mailing list for more like this
Ranked: The 20 Most Air-Polluted Cities on Earth
This was originally posted on Elements. Sign up to the free mailing list to get beautiful visualizations on real assets and resource megatrends each week.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), almost the entire global population (99%) breathes air that exceeds WHO air quality limits.
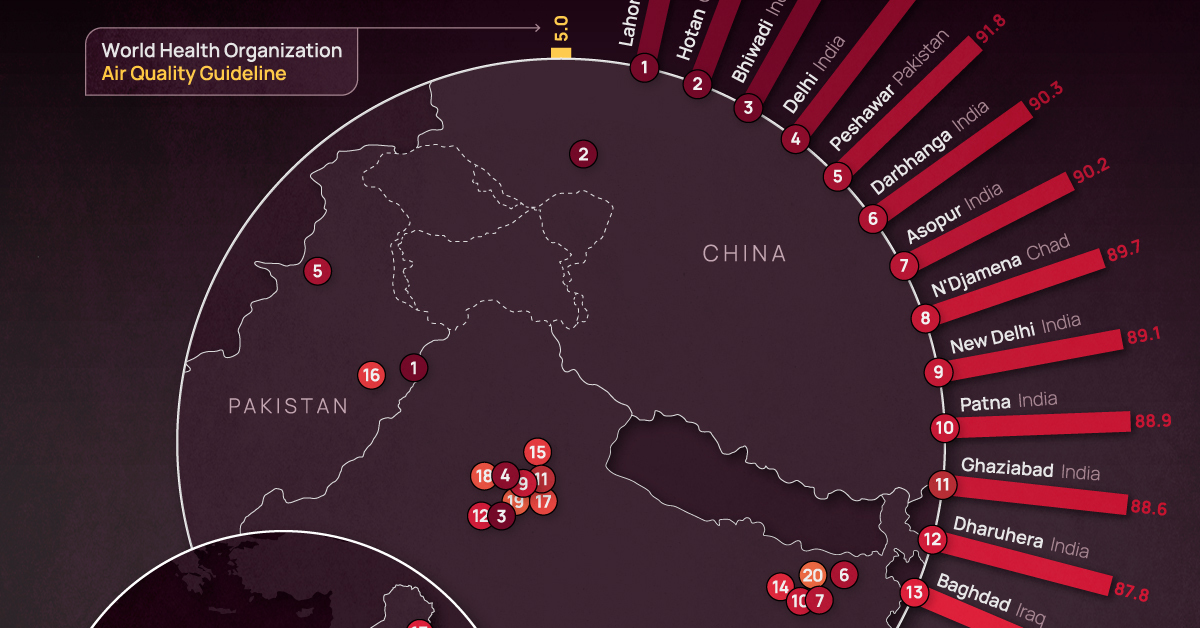
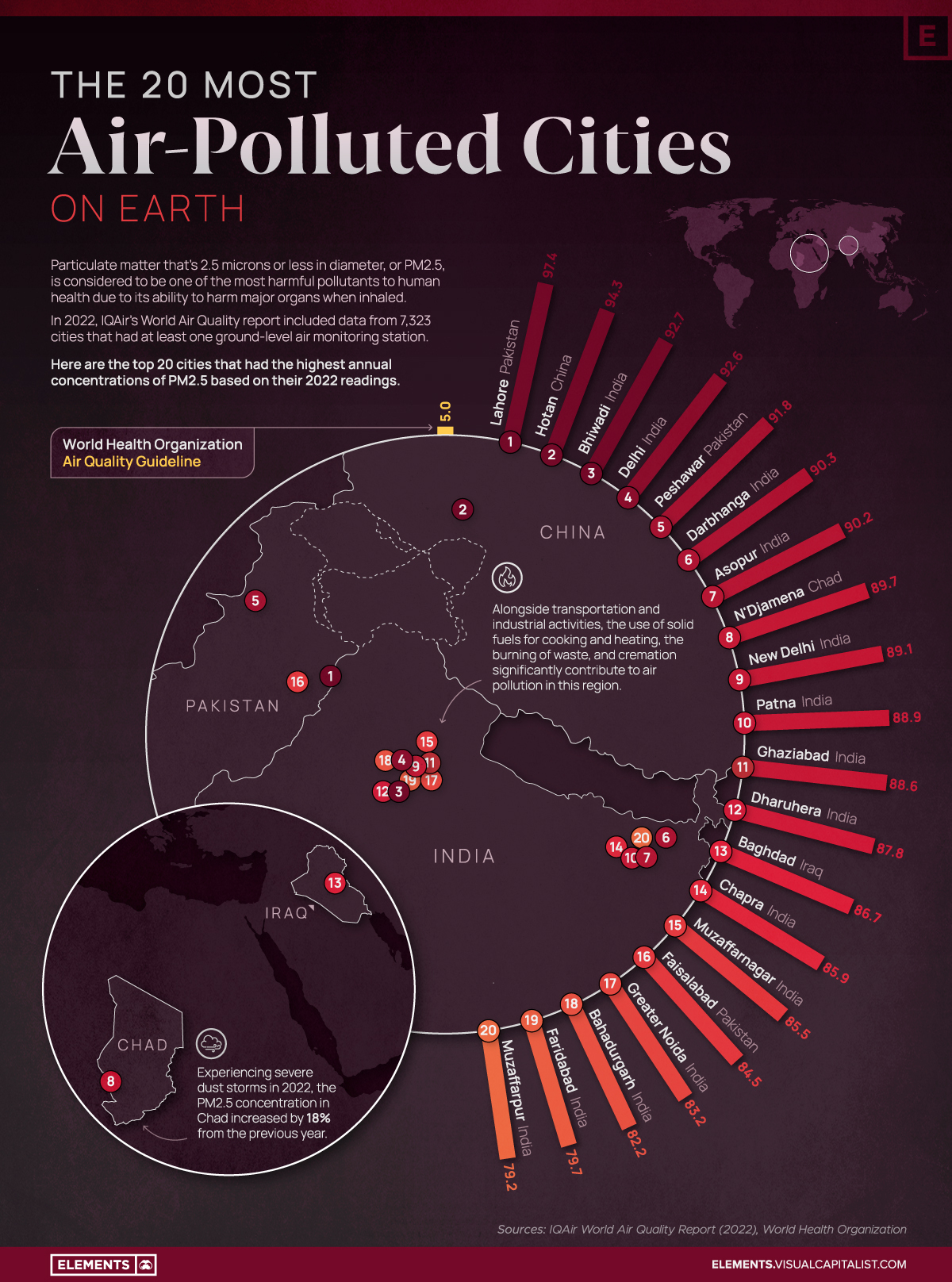
In the above map, we use 2022 average PM2.5 concentrations from IQAir’s World Air Quality Report to visualize the most air-polluted major cities in the world.
World’s Air Pollution Hot Spots
As one of the standard air quality indicators used by the WHO, the PM2.5 concentration refers to the quantity of fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less in a given volume of air.
Fine particulate matter that is this small can penetrate the lungs when inhaled and enter the bloodstream, affecting all major organs.
Based on annual average PM2.5 concentrations (μg/m³) in 2022, here are the most polluted cities in the world.
| Rank | City | 2022 average PM2.5 concentration (μg/m³) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇵🇰 Lahore, Pakistan | 97.4 |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 Hotan, China | 94.3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Bhiwadi, India | 92.7 |
| 4 | 🇮🇳 Delhi, India | 92.6 |
| 5 | 🇵🇰 Peshawar, Pakistan | 91.8 |
| 6 | 🇮🇳 Darbhanga, India | 90.3 |
| 7 | 🇮🇳 Asopur, India | 90.2 |
| 8 | 🇹🇩 N'Djamena, Chad | 89.7 |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi, India | 89.1 |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 Patna, India | 88.9 |
| 11 | 🇮🇳 Ghaziabad, India | 88.6 |
| 12 | 🇮🇳 Dharuhera, India | 87.8 |
| 13 | 🇮🇶 Baghdad, Iraq | 86.7 |
| 14 | 🇮🇳 Chapra, India | 85.9 |
| 15 | 🇮🇳 Muzaffarnagar, India | 85.5 |
| 16 | 🇵🇰 Faisalabad, Pakistan | 84.5 |
| 17 | 🇮🇳 Greater Noida, India | 83.2 |
| 18 | 🇮🇳 Bahadurgarh, India | 82.2 |
| 19 | 🇮🇳 Faridabad, India | 79.7 |
| 20 | 🇮🇳 Muzaffarpur, India | 79.2 |
With numbers these high, the concentration of some or all of the following pollutants are at dangerous levels in these cities:
- Ground-level ozone
- Particulate matter
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
At the top of the list, Lahore in Pakistan has a combination of high vehicle and industrial emissions, as well as smoke from brick kilns, crop residue, general waste burning, and dust from construction sites.
Air pollution levels can also be impacted by practices such as large-scale tree removal in order to build new roads and buildings.
As a result of its growing population and rapidly expanding industrial sector, India has 14 cities on the list, outpacing China, formerly considered the world’s number one air pollution source.
The only African country on the list, Chad, experienced severe dust storms in 2022 that resulted in an 18% increase in PM2.5 concentration in 2022 compared to the previous year.
The Cost of Poor Air Quality
Poor air quality is one of the leading causes of early deaths worldwide, just behind high blood pressure, tobacco use, and poor diet.
According to a 2020 study by the Health Effects Institute, 6.67 million people died as a result of air pollution in 2019.
In addition to the millions of premature deaths each year, the global cost of health damages associated with air pollution currently sits at $8.1 trillion.
Green
How Carbon Credits Can Help Close the Climate Funding Gap
To keep a 1.5℃ world within reach, global emissions need to fall by as much as 45% by 2030, and carbon credits could help close the gap.
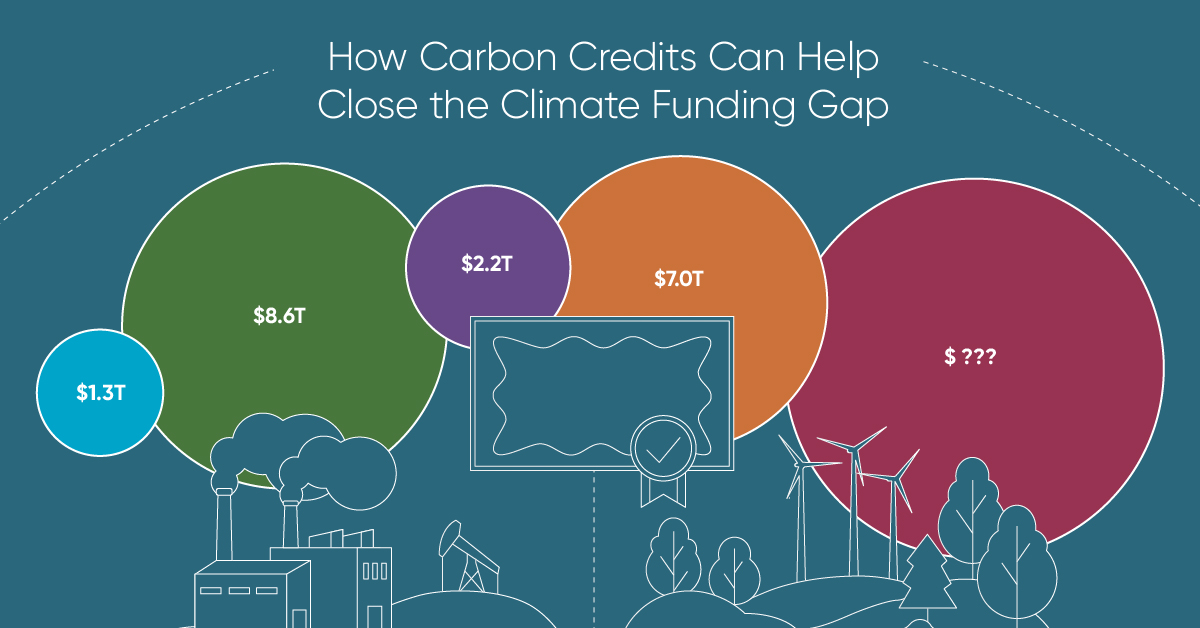
How Carbon Credits Can Help Close the Climate Funding Gap
Governments around the world have committed to the goals of the Paris Agreement, but their climate pledges are insufficient. To keep a 1.5℃ world within reach, global emissions need to fall by as much as 45% by 2030.
Bold and immediate action is essential, but so are resources that will make it happen.
In this graphic, we have partnered with Carbon Streaming to look at the role that the voluntary carbon market and carbon credits can play in closing that gap.
More Funds are Needed for Climate Finance
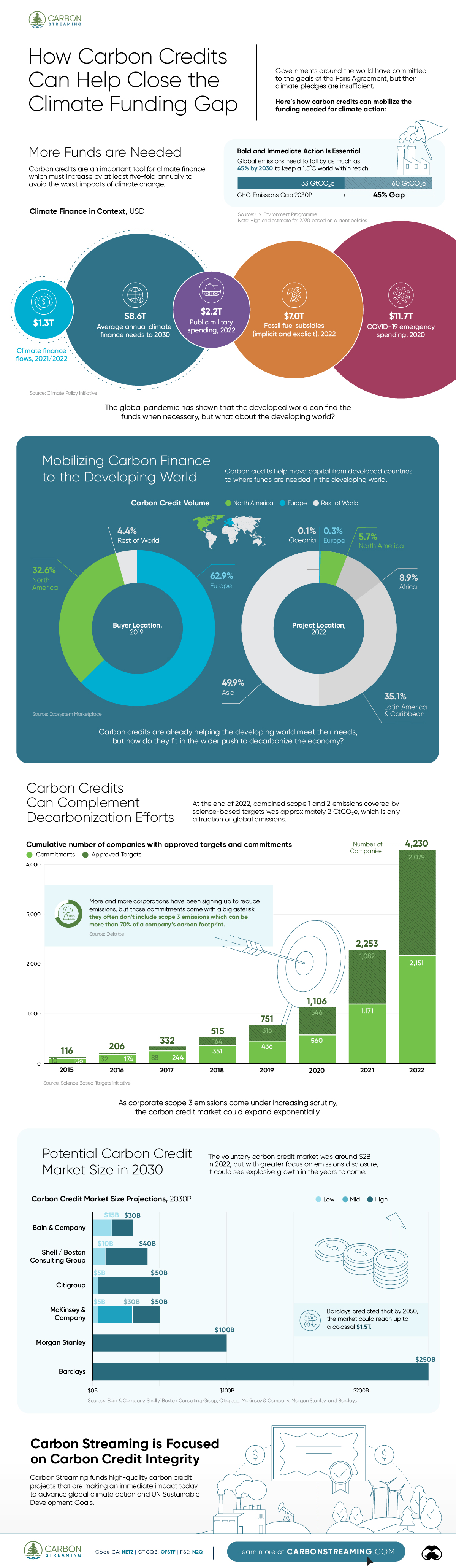
According to data from the Climate Policy Initiative, climate finance, which includes funds for both adaptation and mitigation, needs to increase at least five-fold, from $1.3T in 2021/2022, to an average $8.6T annually until 2030, and then to just over $10T in the two decades leading up to 2050.
That adds up to a very large number, but consider that in 2022, $7.0T went to fossil fuel subsidies, which almost covers the annual estimated outlay. And the world has shown that when pressed, governments can come up with the money, if the global pandemic is any indication.
Mobilizing Carbon Finance to the Developing World
But the same cannot be said of the developing world, where debt, inequality, and poverty reduce the ability of governments to act. And this is where carbon credits can play an important role. According to analyses from Ecosystem Marketplace, carbon credits help move capital from developed countries, to where funds are needed in the developing world.
For example, in 2019, 69.2% of the carbon credits by volume in the voluntary carbon market were purchased by buyers in Europe, and nearly a third from North America. Compare that to over 90% of the volume of carbon credits sold in the voluntary carbon market in 2022 came from projects that were located outside of those two regions.
Carbon Credits Can Complement Decarbonization Efforts
Carbon credits can also complement decarbonization efforts in the corporate world, where more and more companies have been signing up to reduce emissions. According to the 2022 monitoring report from the Science Based Targets initiative, 4,230 companies around the world had approved targets and commitments, which represented an 88% increase from the prior year. However, as of year end 2022, combined scope 1 and 2 emissions covered by science-based targets totaled approximately 2 GtCO2e, which represents just a fraction of global emissions.
The fine print is that this is just scope 1 and 2 emissions, and doesn’t include scope 3 emissions, which can account for more than 70% of a company’s total emissions. And as these emissions come under greater and greater scrutiny the closer we get to 2030 and beyond, the voluntary carbon credit market could expand exponentially to help meet the need to compensate for these emissions.
Potential Carbon Credit Market Size in 2030
OK, but how big? In 2022, the voluntary carbon credit market was around $2B, but some analysts predict that it could grow to between $5–250 billion by 2030.
| Firm | Low Estimate | High Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Bain & Company | $15B | $30B |
| Barclays | N/A | $250B |
| Citigroup | $5B | $50B |
| McKinsey & Company | $5B | $50B |
| Morgan Stanley | N/A | $100B |
| Shell / Boston Consulting Group | $10B | $40B |
Morgan Stanley and Barclays were the most bullish on the size of the voluntary carbon credit market in 2030, but the latter firm was even more optimistic about 2050, and predicted that the voluntary carbon credit market could grow to a colossal $1.5 trillion.
Carbon Streaming is Focused on Carbon Credit Integrity
Ultimately, carbon credits could have an important role to play in marshaling the resources needed to keep the world on track to net zero by 2050, and avoiding the worst consequences of a warming world.
Carbon Streaming uses streaming transactions, a proven and flexible funding model, to scale high-integrity carbon credit projects to advance global climate action and UN Sustainable Development Goals.

Learn more at www.carbonstreaming.com.

-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanking the Top 15 Countries by Carbon Tax Revenue
This graphic highlights France and Canada as the global leaders when it comes to generating carbon tax revenue.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
South Asian nations are the global hotspot for pollution. In this graphic, we rank the world’s most polluted countries according to IQAir.
-

 Environment2 weeks ago
Environment2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001
One country is taking reforestation very seriously, registering more than 400,000 square km of forest growth in two decades.
-

 Green3 weeks ago
Green3 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
The country with the most forest loss since 2001 lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
-

 Markets2 months ago
Markets2 months agoThe World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
Here are the largest cocoa producing countries globally—from Côte d’Ivoire to Brazil—as cocoa prices hit record highs.
-

 Environment2 months ago
Environment2 months agoCharted: Share of World Forests by Country
We visualize which countries have the biggest share of world forests by area—and while country size plays a factor, so too, does the environment.
-

 Maps1 week ago
Maps1 week agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share