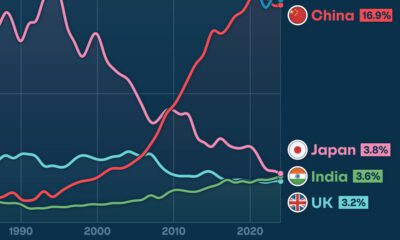
Maps
Mapped: The Expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
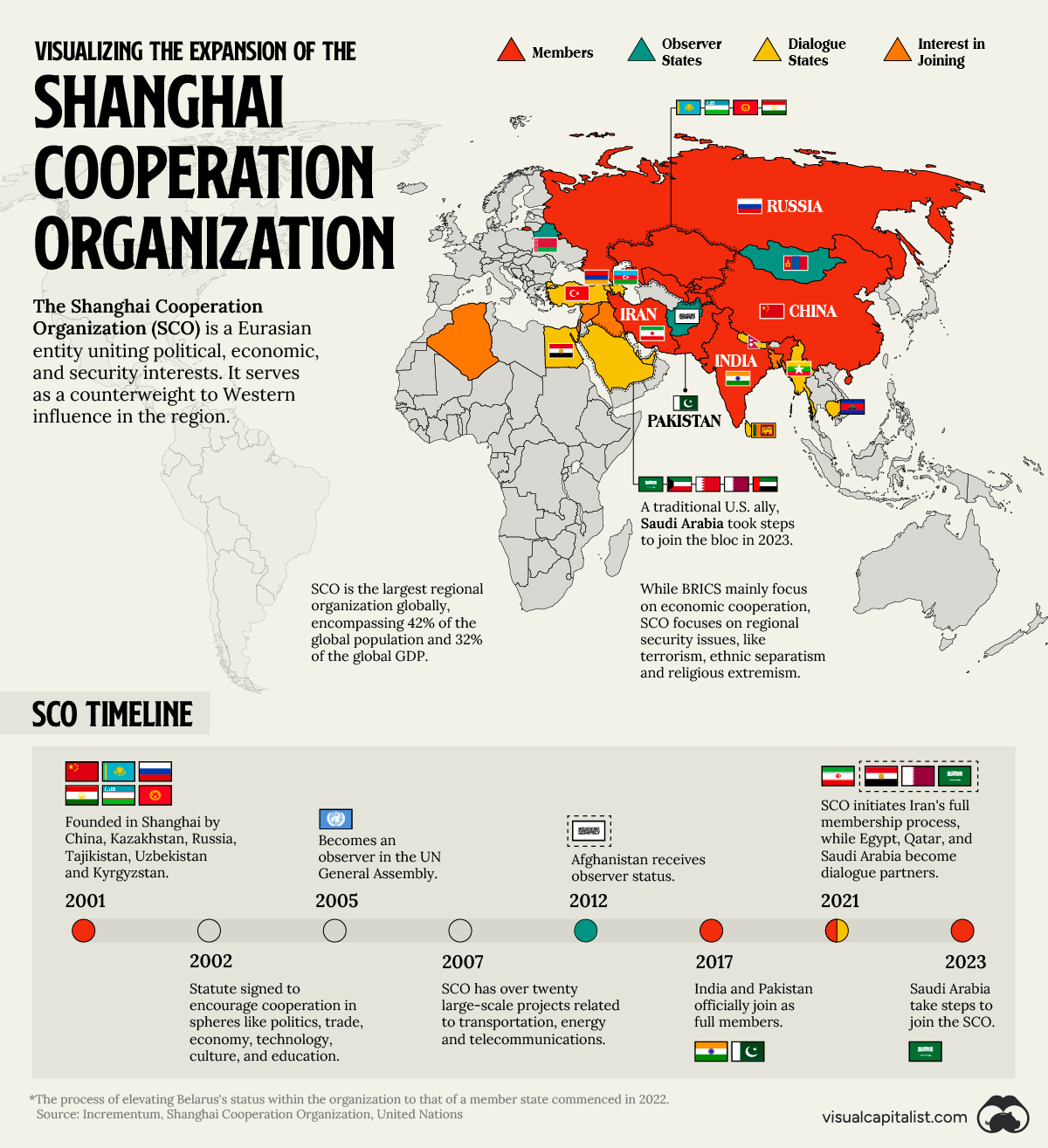
Expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
China has actively pursued the expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), a Eurasian political, economic, and international security entity.
Established in 2001 by Russia, China, and former Soviet states, the organization serves as a counterbalance to Western influence in the region.
The map above uses data from Incrementum, the UN, and the SCO to illustrate the development of the largest regional organization globally.
SCO Timeline
The SCO, formed with objectives such as combating terrorism, promoting border security, strengthening political ties, and expanding economic cooperation, initially included China, Kazakhstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
| Country | Status | Joining date |
|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | Member | 2001 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | Member | 2001 |
| 🇮🇳 India | Member | 2005 |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | Member | 2005 |
| 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | Member | 2005 |
| 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | Member | 2001 |
| 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | Observer | 2012 |
| 🇧🇾 Belarus | Observer | 2015 |
| 🇲🇳 Mongolia | Observer | 2004 |
| 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇦🇲 Armenia | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇧🇭 Bahrain | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇪🇬 Egypt | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | Dialogue Partner | 2015 |
| 🇶🇦 Qatar | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇰🇼 Kuwait | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇲🇻 Maldives | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇳🇵 Nepal | Dialogue Partner | 2016 |
| 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | Dialogue Partner | 2023 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | Dialogue Partner | 2022 |
| 🇹🇷 Turkey | Dialogue Partner | 2013 |
| 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | Dialogue Partner | 2010 |
In 2002, member states ratified the organization statute to encourage political, trade, economic, technological, cultural, and educational collaboration.
Since then, the organization has undertaken over 20 large-scale projects related to transportation, energy, and telecommunications. A notable initiative is China’s expansive Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which aims to rebuild the Silk Road and connect China to Asia, Europe, and beyond through significant infrastructure investments.
The organization has also expanded its geopolitical influence. It attained observer status in the UN General Assembly in 2005 and gave Afghanistan observer status in 2012. Currently, it is working with the interim Taliban administration to include Afghan representatives in its future meetings.
India and Pakistan officially became members of the SCO in 2017, and Iran is in the process of obtaining full-time membership. Egypt and Qatar are dialogue partners, and Saudi Arabia, a traditional U.S. ally, has taken steps to join. Belarus is set to become a member in 2024 after signing a memorandum of obligations.
Furthermore, the organization also plays a crucial role in Chinese military ambitions.
In 2007, the SCO signed an agreement outlining the legal rights and responsibilities for military exercises in another member country.
The agreement allows Chinese armed forces to engage in air-ground combat operations abroad, covering activities like long-distance mobilization, counterterrorism missions, stability maintenance operations, and conventional warfare.
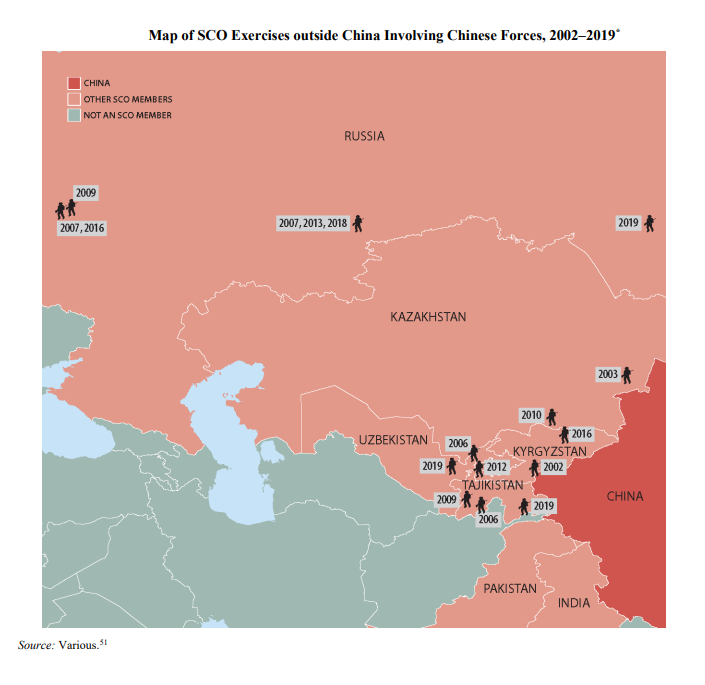
Military presence is particularly important for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), which fears that separatist movements in the Uyghur-dominated autonomous region of Xinjiang could gain support from other Central Asian states.
Implications for the United States
Today, the SCO encompasses 42% of the global population and 32% of the global GDP.
Due to its growing influence, U.S. policymakers have been monitoring the development of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization.
In a 2020 report to the U.S. Congress, the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission highlighted that through the SCO, China is establishing diplomatic relationships and expeditionary capabilities that could support power projection beyond its borders.
According to the document, “there is a significant risk that Beijing may leverage its relationships with SCO countries to limit the ability of U.S. armed forces to operate in Central Asia.”
Nonetheless, the same report mentions that the SCO could serve as a beneficial tool for Central Asian states, offering a platform for cooperation and presenting an alternative to potential domination by Russia, particularly in areas such as energy.
Maps
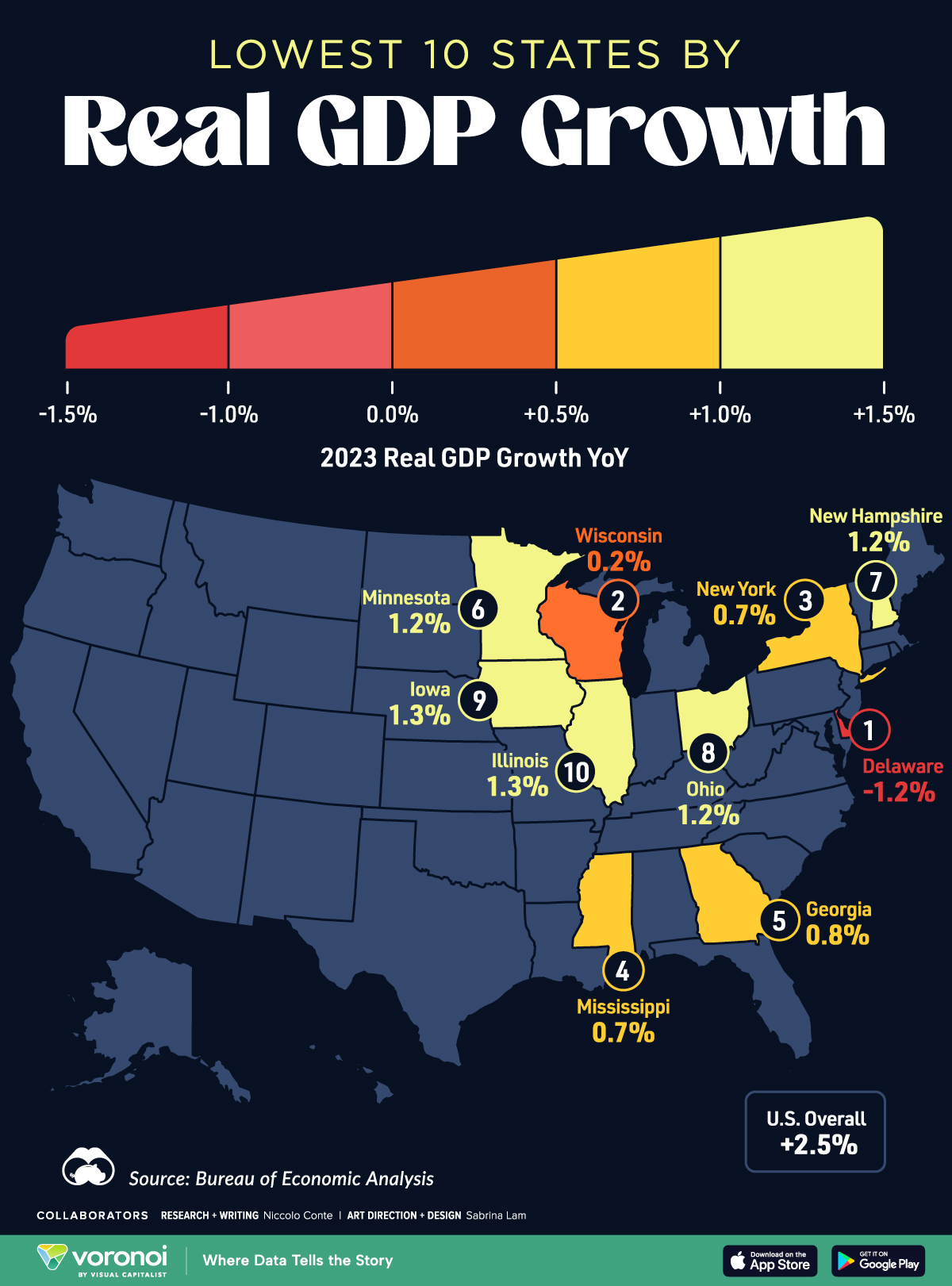
Mapped: The 10 U.S. States With the Lowest Real GDP Growth
In this graphic, we show where real GDP lagged the most across America in 2023 as high interest rates weighed on state economies.

The Top 10 U.S. States, by Lowest Real GDP Growth
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
While the U.S. economy defied expectations in 2023, posting 2.5% in real GDP growth, several states lagged behind.
Last year, oil-producing states led the pack in terms of real GDP growth across America, while the lowest growth was seen in states that were more sensitive to the impact of high interest rates, particularly due to slowdowns in the manufacturing and finance sectors.
This graphic shows the 10 states with the least robust real GDP growth in 2023, based on data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Weakest State Economies in 2023
Below, we show the states with the slowest economic activity in inflation-adjusted terms, using chained 2017 dollars:
| Rank | State | Real GDP Growth 2023 YoY | Real GDP 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delaware | -1.2% | $74B |
| 2 | Wisconsin | +0.2% | $337B |
| 3 | New York | +0.7% | $1.8T |
| 4 | Missississippi | +0.7% | $115B |
| 5 | Georgia | +0.8% | $661B |
| 6 | Minnesota | +1.2% | $384B |
| 7 | New Hampshire | +1.2% | $91B |
| 8 | Ohio | +1.2% | $698B |
| 9 | Iowa | +1.3% | $200B |
| 10 | Illinois | +1.3% | $876B |
| U.S. | +2.5% | $22.4T |
Delaware witnessed the slowest growth in the country, with real GDP growth of -1.2% over the year as a sluggish finance and insurance sector dampened the state’s economy.
Like Delaware, the Midwestern state of Wisconsin also experienced declines across the finance and insurance sector, in addition to steep drops in the agriculture and manufacturing industries.
America’s third-biggest economy, New York, grew just 0.7% in 2023, falling far below the U.S. average. High interest rates took a toll on key sectors, with notable slowdowns in the construction and manufacturing sectors. In addition, falling home prices and a weaker job market contributed to slower economic growth.
Meanwhile, Georgia experienced the fifth-lowest real GDP growth rate. In March 2024, Rivian paused plans to build a $5 billion EV factory in Georgia, which was set to be one of the biggest economic development initiatives in the state in history.
These delays are likely to exacerbate setbacks for the state, however, both Kia and Hyundai have made significant investments in the EV industry, which could help boost Georgia’s manufacturing sector looking ahead.
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State
-
 Misc6 days ago
Misc6 days agoVisualized: Aircraft Carriers by Country
-

 Culture7 days ago
Culture7 days agoHow Popular Snack Brand Logos Have Changed
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
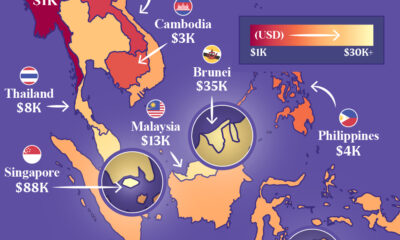
 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country